
How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Oil Cylinder for Your Needs?
Choosing the right Hydraulic Oil Cylinder can be a daunting task. Industry expert John Smith emphasizes, “Selecting the correct cylinder is vital for performance and safety.” His words highlight the importance of making informed choices.
Hydraulic Oil Cylinders are essential components in various machinery and vehicles. They enable powerful movements and precise control. However, with many options available, confusion arises. Factors such as size, material, and application must be considered carefully.
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial. Not all hydraulic cylinders serve the same purpose. The right choice can enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance needs. Reflecting on past choices may reveal gaps in understanding. Gaining knowledge about these cylinders can lead to better decisions.

Understanding the Basics of Hydraulic Oil Cylinders
Understanding hydraulic oil cylinders is essential for effective operation in various applications. These cylinders convert hydraulic energy into linear motion. They are common in construction, manufacturing, and automotive sectors. Knowing their components and functions helps in selecting the right one for a specific task.
Hydraulic oil cylinders consist of a piston, rod, and cylinder chamber. The oil creates pressure that moves the piston. Corrosion resistance and sealing are vital for efficiency and longevity. A well-performing cylinder minimizes downtime. However, poor maintenance can lead to leakage or failures. Regular checks on oil quality and cylinder condition are crucial.
Choosing the appropriate hydraulic oil is just as important. Different applications require specific oil types for optimal performance. A mismatch can cause inefficiencies. Thickness and additives vary, influencing the cylinder's operation. Understanding the specific requirements will greatly enhance performance and reliability. It's a learning process, and even experts can overlook some details. Being mindful of these aspects ensures a successful hydraulic system.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Hydraulic Oil Cylinder
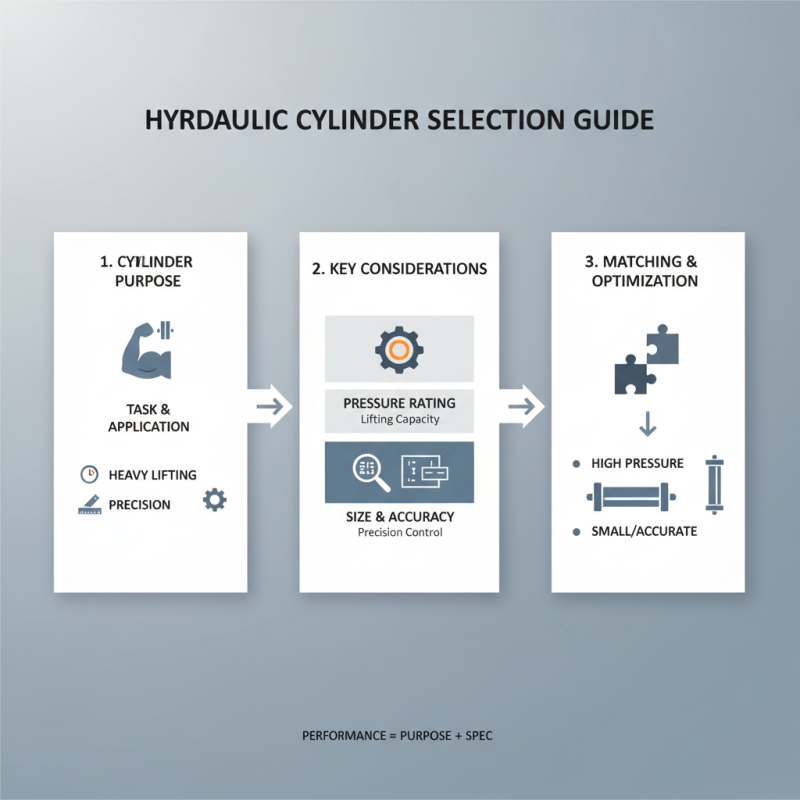
Choosing the right hydraulic oil cylinder requires careful consideration. Start with the cylinder's purpose. Understand what tasks you need it to perform. Different applications need different specifications. For instance, lifting heavy loads may require a cylinder with higher pressure ratings. Meanwhile, precision tasks might need smaller, more accurate cylinders.
Next, consider the environment where the cylinder will operate. Will it be exposed to extreme temperatures or harsh conditions? Selecting a cylinder with proper seals and materials is crucial. Poor choices could lead to rapid wear or failure. Maintenance is another factor. Some cylinders demand frequent checks; others are low-maintenance. Think about what fits your operational capabilities.
Don’t overlook size and stroke length. A cylinder that’s too big may cause space issues. Conversely, if it's too small, it won’t get the job done efficiently. It’s easy to underestimate these factors. Test options before making a final decision. Real-world trials can reveal limitations or advantages you hadn’t considered. In the end, a misstep in choosing can create significant headaches down the line.
Types of Hydraulic Oil Cylinders and Their Applications
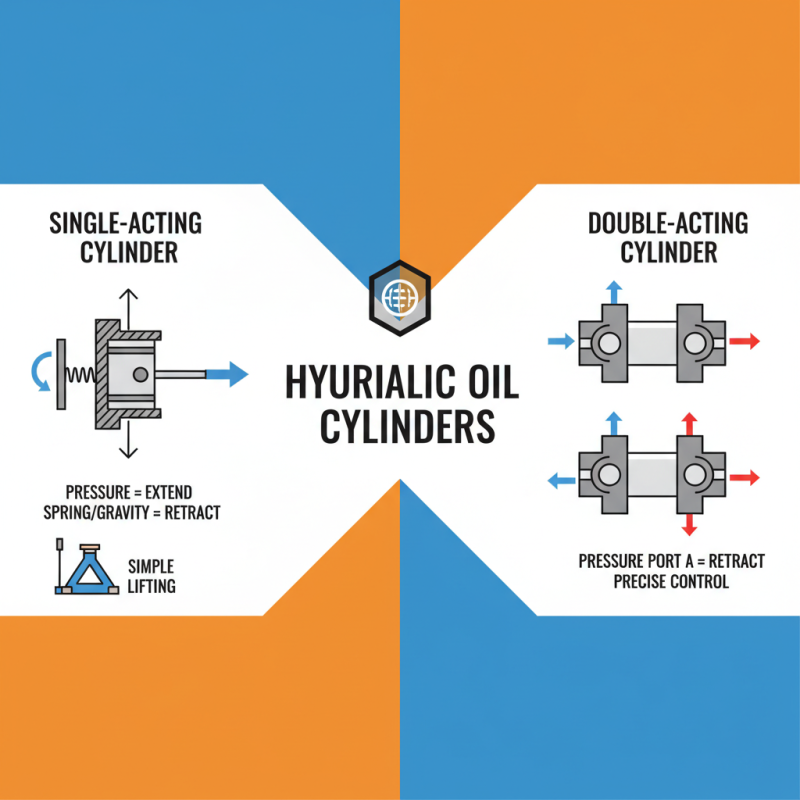
Hydraulic oil cylinders come in various types, each suited for specific applications. The most common types include single-acting and double-acting cylinders. Single-acting cylinders use hydraulic pressure for movement in one direction, while a return spring or gravity helps in repositioning. These are often found in simple applications like car jacks.
On the other hand, double-acting cylinders can push and pull, making them versatile for complex tasks. They’re widely used in construction machinery and manufacturing equipment. It's essential to assess your project before selecting a type. Sometimes, users opt for the wrong cylinder, leading to inefficiencies and potential failures.
Another consideration is the size and force capacity. An oversized cylinder can lead to wasted energy. Conversely, a smaller one may not produce enough force for the job. Users often overlook the importance of stroke length and mounting style. These factors significantly affect overall performance. It’s vital to evaluate your needs carefully to avoid costly mistakes.
How to Determine the Right Specifications for Your Needs
When choosing a hydraulic oil cylinder, determining the right specifications is critical. Start by assessing the application. Are you using it for lifting, pushing, or pulling? This affects the size and pressure requirements. Different tasks demand different forces. An inadequate cylinder can lead to inefficiency. Sometimes, people underestimate the load. This could cause failure.
Next, consider the environment. Will the cylinder be exposed to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances? These conditions can deteriorate the material. Selection of suitable seals and coatings becomes essential. High temperatures may require special materials. Rain or chemicals could compromise regular cylinders.
Finally, think about the cycle rate, which involves the number of times the cylinder will operate. Higher cycle rates demand more durable components. It’s crucial to balance cost and performance. A cheap cylinder may save money upfront but could lead to repetitive failures. Reflecting on potential trade-offs can improve your decision-making.
How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Oil Cylinder for Your Needs?
| Specification | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Bore Diameter | The internal diameter of the cylinder. | Critical for determining the force output. |
| Stroke Length | The distance the cylinder can extend. | Influences the range of motion for the application. |
| Working Pressure | The maximum pressure the cylinder can handle. | Essential for safe and efficient operation. |
| Mounting Style | How the cylinder is attached to the machinery. | Determines compatibility with existing setups. |
| Cylinder Type | Type of hydraulic cylinder (e.g., double-acting, single-acting). | Affects performance and application suitability. |
| Material | Material used for the cylinder construction. | Impacts durability and resistance to environmental factors. |
Maintenance Tips for Extending the Life of Hydraulic Oil Cylinders
Proper maintenance of hydraulic oil cylinders is crucial for longevity. Regular inspections help identify leakages or wear. Studies show that 30% of hydraulic system failures are due to improper maintenance. Check seals and fittings often. Replace any damaged parts to avoid serious issues later.
Flushing the hydraulic system can remove contaminants. This process should typically occur every 3,000 hours of operation. Furthermore, monitoring oil levels is essential. Low oil levels can lead to overheating and damage. The use of filters can improve oil quality, reducing wear by up to 50%.
Temperature also plays a role. Keep the operating temperature within recommended limits. High temperatures can degrade oil quickly, reducing its effectiveness. If not carefully monitored, this could lead to costly repairs. Remember, neglecting maintenance today can lead to larger problems tomorrow.
Hydraulic Oil Cylinder Maintenance: Usage Hours vs. Maintenance Frequency
Related Posts
-

2026 Top Hydraulic Oil Cylinder Applications and Benefits?
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Hydraulic Oil Cylinder for Your Needs
-

7 Solid Reasons to Choose Hydraulic Oil Cylinders for Your Industrial Needs
-
Why Choose Hydraulic Oil Cylinder for Your Machinery Needs?
-

Essential Checklist for Selecting the Right Hydraulic Oil Cylinder for Your Needs
-

Top Strategies for Enhancing Performance of Hydraulic Oil Cylinders
